『化学⑭』エンプラ②PC ポリカーボネート 河東丈二
- nakata513
- 2022年11月21日
- 読了時間: 9分
更新日:2022年11月29日
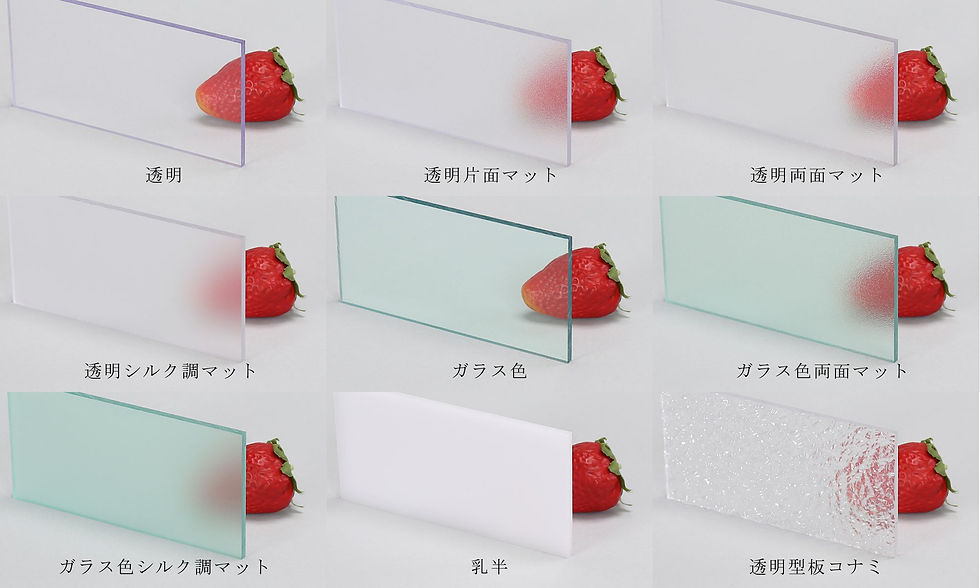
ポリカーボネート(PC)
ポリカーボネート (PC) は、カーボネート官能基を持つ透明な熱可塑性樹脂です。 その高い強度により、衝撃や破損に耐性があります。 軽量なのでガラスの代替品として最適です。 PCを溶かし、高圧で金型に押し込み、目的の形状に成形します。 環境に配慮した処理とリサイクルが可能なため、広く使用されています。
ポリカーボネートは、カーボネート基 (–O–(C=O)–O–) によって結合された有機官能基を持つ、高性能の強靭で非晶質で透明な熱可塑性ポリマーであり、独自の特性の組み合わせを提供します。 PC は、次のような独自の機能により、エンジニアリング プラスチックとして広く使用されています。
高衝撃強度
高い寸法安定性
とりわけ優れた電気特性
ポリメチルメタクリレート(PMMA、アクリル)と特性は似ていますが、ポリカーボネートの方が強度が高く、使用温度範囲が広い(融点:155℃)反面、価格が高くなります。 PC は特定のポリマーとの相溶性に優れているため、PC/ABS、PC/PET、PC/PMMA などのブレンドで広く使用されています。 一般的な用途には、コンパクト ディスク、安全ヘルメット、防弾ガラス、車のヘッドランプ レンズ、哺乳瓶、屋根材、窓ガラスなどがあります。
ポリカーボネートの主な特徴と性質
PC は、その汎用性の高い特性、環境に優しい処理、およびリサイクル可能性から、業界でよく知られており、広く使用されている理想的な素材です。独自の化学的および物理的特性を備えているため、ガラス、PMMA、および PE に適しています。
PC プロパティについて詳しく説明します。
靭性と高い衝撃強度 - ポリカーボネートは強度が高く、衝撃や破損に強く、高い信頼性と性能が要求される用途で安全性と快適性をさらに提供します。ポリマーの密度は 1.2 ~ 1.22 g/cm3 で、140°C まで、-20°C まで靭性を維持します。また、PC は実質的に壊れません。
透過率 – PC は非常に透明なプラスチックで、ガラスと同じくらい 90% 以上の光を透過します。ポリカーボネート シートは、エンド ユーザーの用途に応じてカスタマイズできる幅広い色合いで入手できます。
軽量 - この機能により、ガラスと比較して、OEM は事実上無限の可能性を設計できます。また、このプロパティにより、効率が向上し、設置プロセスが容易になり、全体的な輸送コストが削減されます。
紫外線からの保護 – ポリカーボネートは、紫外線を遮断し、有害な紫外線から 100% 保護するように設計できます。
光学的性質 - 非晶質構造を持つため、PC は優れた光学特性を提供します。透明なポリカーボネートの屈折率は 1.584 です。
耐薬品性 - ポリカーボネートは、希酸、脂肪族炭化水素、アルコールに対して優れた耐薬品性を示します。オイルおよびグリースに対する中程度の耐薬品性。 PC は、希釈アルカリ、芳香族およびハロゲン化炭化水素によって容易に攻撃されます。メーカーは、化学的性質に影響を与えない特定の洗浄剤で PC シートを洗浄することを推奨しています。研磨性のアルカリ洗浄剤に敏感です。
耐熱性 - 優れた耐熱性を提供するポリカーボネートは、135°C まで熱的に安定しています。材料特性に影響を与えることなく、難燃剤を添加することで、さらに耐熱性を向上させることができます。
強みとして
透明性が高い。 ガラスと同等の光透過率を提供
-20℃でも高い靭性
140°Cまでの高い機械的保持
本質的に難燃性
水や温度の影響を受けない優れた電気絶縁性を提供
耐摩耗性に優れています
繰り返しの蒸気滅菌に耐える
制限事項
炭化水素や塩基による攻撃を受けやすい
60°Cを超える水に長時間さらされると、機械的特性が低下し始めます
加工前に十分な乾燥が必要
疲労耐久性が低い
紫外線を浴びると黄ばみやすい
特性を最適化するための添加剤または熱可塑性ブレンドの使用
ポリカーボネートの耐クリープ性は、ガラス繊維または炭素繊維の補強材を追加することで改善できます。 GF 補強材の 5 ~ 40% は、210°F の高温で最大 28 MPa の耐クリープ性を向上させることができます。強化グレードは、標準の PC グレードと比較して、引張弾性率、曲げ強度、引張強度が優れています。
添加剤を追加すると、難燃性、熱安定性、UV 光と色の安定性、およびその他のいくつかの特性を改善できます。コーティングされたポリカーボネート シートは、耐候性、耐傷性、耐薬品性にも優れています。
ベンゾトリアゾールに基づく安定剤は、PC を UV 光から安定させ、UV 劣化から保護するのに役立ちます。
亜リン酸エステルベースの安定剤は、ポリカーボネートの熱安定性を改善するのに有効であることが知られています。
必要な UL 性能を達成し、LOI を高め、PC 製品の燃焼熱を下げるために、ハロゲン化、リン系、シリコーン系などのいくつかの難燃剤が広く使用されています。
ポリカーボネートブレンドは、性能と生産性の適切なバランスを提供することで商業的に成功しています。
PC/ポリエステル ブレンド: これらの合金は、高い耐薬品性が必要な用途に適しています。 PC/PBT ブレンドは、PBT の結晶性が高いため、PC/PET ブレンドよりも高い耐薬品性を提供しますが、PET ブレンド グレードは優れた耐熱性を提供します。
PC/ABS ブレンド: PC の靭性と高い耐熱性を ABS の延性と加工性と組み合わせることで、優れた特性の組み合わせが実現します。
PCはどのように製造されていますか?

ポリカーボネートは、ビスフェノール A (BPA; C15H16O2) とホスゲン (COCl2) の縮重合によって製造されます。
製造方法
ポリカーボネート部品を製造する一般的な方法
押し出す
射出成形
中空成形、吹込み成形
熱成形
PCを溶かし、高圧で金型に押し込み、目的の形状に成形します。処理前の乾燥を強くお勧めします: 120°C で 2 ~ 4 時間。目標水分含有量は、最大 0.02% にする必要があります。
材料の劣化を避けるため、理想的な最大滞留時間は、選択した溶融温度に応じて 6 ~ 12 分です。ポリカーボネート加工に関与する 2 つの主要な技術は、射出成形と押出です。
射出成形
射出成形は、ポリカーボネートとそのブレンドから作られた部品を製造するために最もよく使用される方法です。ポリカーボネートは粘性が高いため、通常は高温で処理して粘度を下げます。このプロセスでは、高温のポリマー溶融物が高圧で金型に押し込まれます。金型が冷えると、溶融ポリマーに望ましい形状と特性が与えられます。このプロセスは、通常、ポリカーボネートのボトル、プレートなどの製造に使用されます。ポリカーボネートは流動性の低いプラスチックであるため、肉厚が薄すぎてはなりません。
Comprehensive Guide on Polycarbonate (PC) Joji Kawahigashi
Polycarbonate (PC) is a transparent thermoplastic with carbonate functional groups. Its high strength makes it resistant to impact and fracture. It is lightweight so an excellent alternate to glass. PC is melted and forced into a mold with high pressure to give it the desired shape. It is widely used owing to its eco-friendly processing and recyclability.
Polycarbonate is a high-performance tough, amorphous and transparent thermoplastic polymer with organic functional groups linked together by carbonate groups (–O–(C=O)–O–) and offers a unique combination of properties. PC is popularly used as an engineering plastic owing to its unique features that include:
High impact strength High dimensional stability Good electrical properties amongst others
Though the characteristics of polycarbonate are similar to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA, acrylic), but polycarbonate is stronger, usable in a wider temperature range (Melting point: 155°C) but more expensive. As PC shows excellent compatibility with certain polymers, it is widely used in blends, such as PC/ABS, PC/ PET, PC/PMMA. Some of the common applications are compact disc, safety helmets, bullet-proof glass, car headlamp lenses, baby feeding bottles, roofing and glazing etc.
Main Characteristics and Properties of Polycarbonate
PC is an ideal material well known and widely used in the industry for its versatile characteristics, eco-friendly processing and recyclability. Comprising a unique set of chemical and physical properties makes it suitable over glass, PMMA and PE.
Let’s discuss PC properties in detail:
Toughness and High Impact Strength – Polycarbonate has high strength making it resistant to impact and fracture, and further providing safety and comfort in applications that demand high reliability and performance. The polymer has density 1.2 – 1.22 g/cm3, maintains toughness upto 140°C and down to -20°C. Also, PCs are virtually unbreakable.
Transmittance – PC is an extremely clear plastic that can transmit over 90% of light as good as glass. Polycarbonate sheets are available in a wide range of shades that can be customized depending on an end-user application.
Lightweight – This feature allows virtually unlimited possibilities to OEMs to design as compared with glass. The property also allows to increase efficiency, make installation process easier and reduce overall transportation costs.
Protection from UV Radiations – Polycarbonates can be designed to block ultraviolet radiation and provide 100% protection from harmful UV rays.
Optical Nature - For having amorphous structure, PC offers excellent optical properties. The refractive index of clear polycarbonate is 1.584.
Chemical Resistance – Polycarbonate exhibits good chemical resistance against diluted acids, aliphatic hydrocarbons and alcohols; moderate chemical resistance against oils and greases. PC is readily attacked by diluted alkalis, aromatic and halogenated hydrocarbons. Manufacturers recommend to clean PC sheets with certain cleaning agents which do not affect its chemical nature. It is sensitive to abrasive alkaline cleaners.
Heat Resistance - Offering good heat resistance, Polycarbonates are thermally stable up to 135°C. Further heat resistance can be improved by adding flame retardants without impacting material properties.
Strengths
Highly transparent. Offers light transmission as good as glass
High toughness even down to -20°C
High mechanical retention up to 140°C
Intrinsically flame retardant
Offers good electrical insulation properties that are not influenced by water or temperature
Possesses good abrasion resistance
Can withstand repeated steam sterilizations
Limitation
Easily attacked by hydrocarbons and bases
Post prolonged exposure to water at over 60°C, their mechanical properties start to degrade
Proper drying is required before processing
Low fatigue endurance
Yellowing tendency post exposure to UV
Use of Additives or Thermoplastic Blends to Optimize Properties
Polycarbonates’ creep resistance can be improved with the addition of glass- or carbon-fiber reinforcements. 5-40% of GF reinforcements can improve creep resistance upto 28 MPa at temperature as high as 210°F. Reinforced grades have better tensile modulus, flexural- & tensile strength as compared to standard PC grades.
Adding additives can improve flame retardancy, thermal stability, UV light and color stability and several other properties. Coated polycarbonates sheets also show better weatherability, and mar- and chemical resistance.
Stabilizers based on benzotriazole are useful to stabilize PC against UV light and protect from UV degradation.
Phosphorous acid esters-based stabilizers are known to be effective to improve thermal stability of polycarbonate.
Several flame retardants, such as halogenated, phosphorous-based and silicone-based are widely used to attain the required UL performance, increase LOI and reduce the heat of combustion for PC products.
Polycarbonate blends are successful commercially for providing a right balance between performance and productivity.
PC/Polyester Blends: These alloys are suitable for applications where high chemical resistance is required. PC/PBT blends offer higher chemical resistance than PC/PET blends due to PBT’s higher crystalline behavior whereas PET blended grades offer superior heat resistance.
PC/ABS Blends: PC’s toughness and high heat resistance combined with ABS ductility and processability provide an excellent combination of properties.
How PC is Manufactured?
Polycarbonates are manufactured by condensation polymerization of bisphenol A (BPA; C15H16O2) and phosgene (COCl2).
Common Methods to Produce Polycarbonate Parts
Extrusion
Injection molding
Blow molding
Thermoforming
PC is melted and forced into a mold with high pressure to give it the desired shape. Drying before processing is highly recommended: 2-4 hr at 120°C. Target moisture content should be a maximum of 0.02%.
In order to avoid material degradation, the ideal maximum residence time is between 6 and 12 minutes depending on the selected melt temperature. Two major techniques involved in polycarbonate processing are injection molding and extrusion.
Injection Molding
Injection molding is most often used method to produce parts made from polycarbonates and their blends. Since polycarbonate is highly viscous, it is usually processed at high temperature to reduce its viscosity. In this process, the hot polymer melt is pressed through into a mold with high pressure. The mold when cools, gives the molten polymer its desired shape and characteristics. This process is generally used to manufacture polycarbonate bottles, plates etc. Since polycarbonate is a poor-flowing plastic, wall thickness should not be too thin.



Comments